An FB friend referred to this paper https://t.co/ARk9JVoQla
— G V Pavan Kumar (@Pavan_KumarGV) July 20, 2023
and asked a few of us why critical thinking in STEM students is getting affected in India.
This is also a recurring question in my podcast.
Below is my short answer.
What do you think about the problem ? pic.twitter.com/EX1YR9qtFv
Category: academia
Pratidhvani-Humanizing Science: podcast on reflections of Academic Scientist
As an extension of my blog, I am starting a podcast in my individual capacity :
Pratidhvani – Humanizing Science
In several Indian languages, including Kannada, Marathi, Sanskrit, Hindi and many more, the word – Pratidhvani (ಪ್ರತಿಧ್ವನಿ/प्रतिध्वनि) – means resonance, reflection (of sound). Through my podcast, I intend to reflect on my thoughts as an academic scientist on some topics related to science, technology, history and philosophy of science. Listen to my first podcast, and let me know what you think.
References :
Kumar, G.V.P., 2023. Science + History —> better Science. Scatterings. URL https://backscattering.wordpress.com/2023/04/01/science-history-better-science/ (accessed 5.11.23).
Kumar, G.V.P., 2022. 12 Years as a faculty member in India – 12 lessons. Scatterings. URL https://backscattering.wordpress.com/2022/05/25/12-years-as-a-faculty-in-india-12-lessons/ (accessed 5.11.23).
Weinberg, S., 2003. Four golden lessons. Nature 426, 389–389. https://doi.org/10.1038/426389a
Mankutimma’s Aphorisms!!: 789, n.d. . Mankutimma’s Aphorisms!! URL http://mankutimma-aphor.blogspot.com/2012/12/789.html (accessed 5.11.23).
Osaka and Optical Manipulation
Thanks to the invitation of Prof. Hajime Ishihara, I visited Osaka from 29th April to 2nd May 2023.
I arrived in Osaka on Saturday (29th Apr). On 30th Apr (Sunday) I headed out to visit the famous Kiyomizudera Temple in Kyoto with 2 PhD students from Ishihara’s group : Hideki Arahari and Takao Horai

Apart from the temple, we had a wonderful time exploring the Nishiki Market and Kamo river.
On 1st May, I visited Osaka University to officially meet Prof Ishihara, his group and other research groups in the university. We had a wonderful discussion on optical manipulation and major projects related to it especially in Japan, and undoubtedly Osaka has emerged as a major center in optical manipulation.

I was delighted to see so many students and research groups interested in optical trapping/manipulation and related science and technology. I learnt about some very interesting applications of optical manipulation. Also, it was great to see such a great sense of humor in this group of researchers. It was truly amazing.
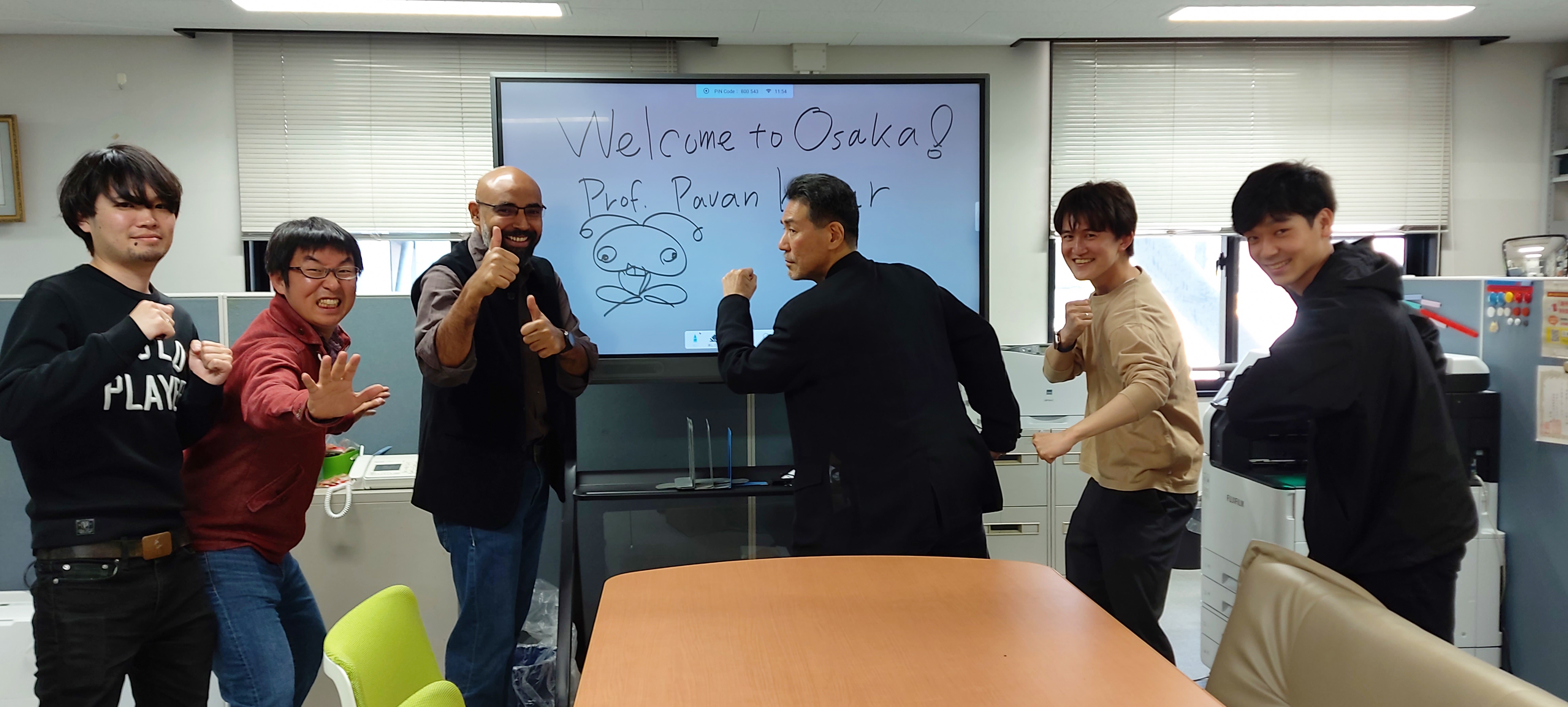

I also visited labs of Prof. Ashida and Prof Ito, and got a very nice overview of their work including optical manipulation in liquid helium and photochemical reactions in an optical trap.
At 4pm, I gave my talk on “Optical Manipulation based on Opto-Thermal Gradients“. I elaborated on the role of absorption and related thermal gradient in optical manipulation. I presented some of our ongoing work on optical manipulation with structured light. The talk was attended by at least 30 to 40 people, and I was informed that students from various groups in Osaka were present (there are a few universities). The quality of questions and the follow up discussion was very good, and really enjoyed it.
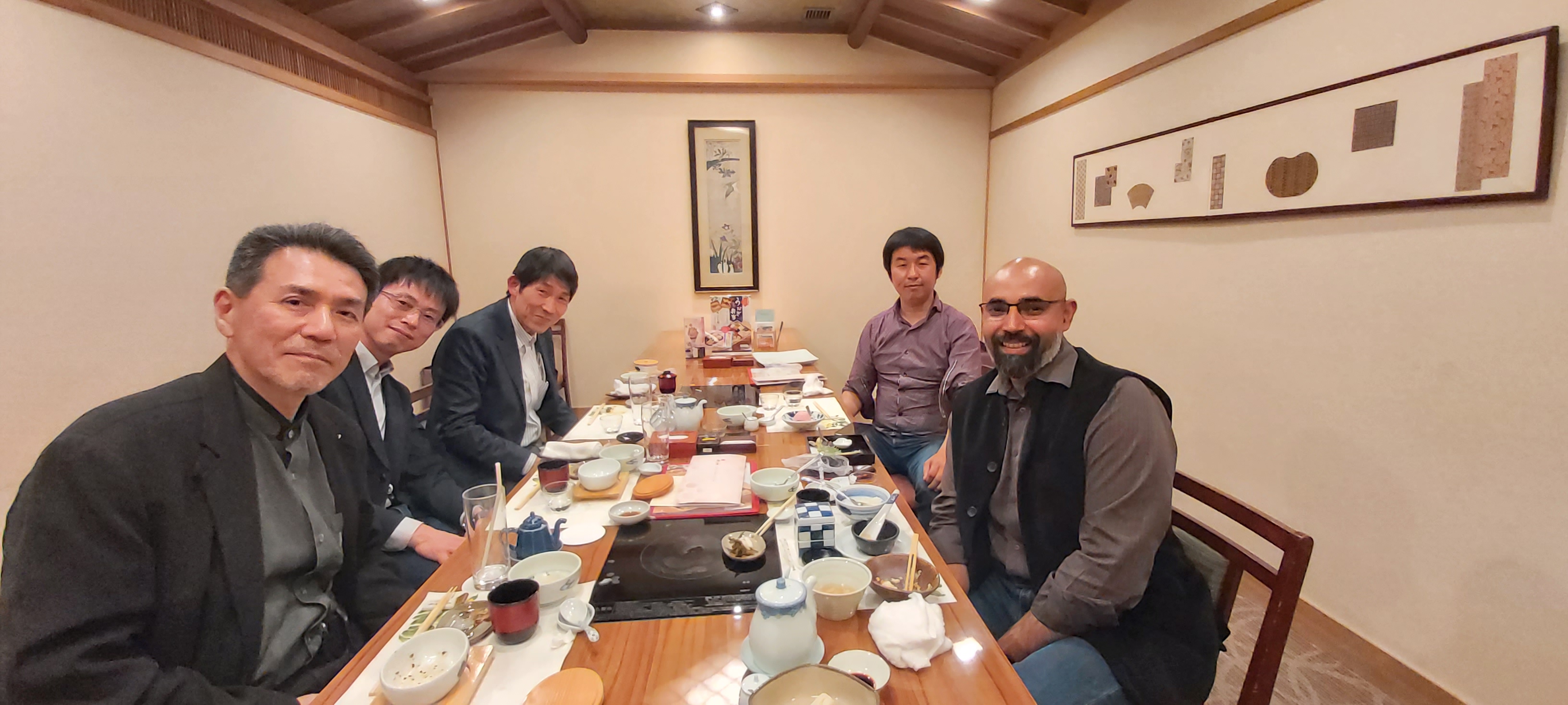
Finally, the day ended with a wonderful dinner at a tofu-themed Japanese restaurant. We had wonderful discussion on history and philosophy in our countries, and was very interesting.

My trajectory in Japan has been Yokohama –> Tokyo –> Okinawa –> Osaka. After 16 days, one conference talk and 4 research seminar across Japan, I am now heading back from Osaka to Tokyo (and writing this blog) on Shinkansen – the bullet train. Tomorrow, I will be leaving to India.
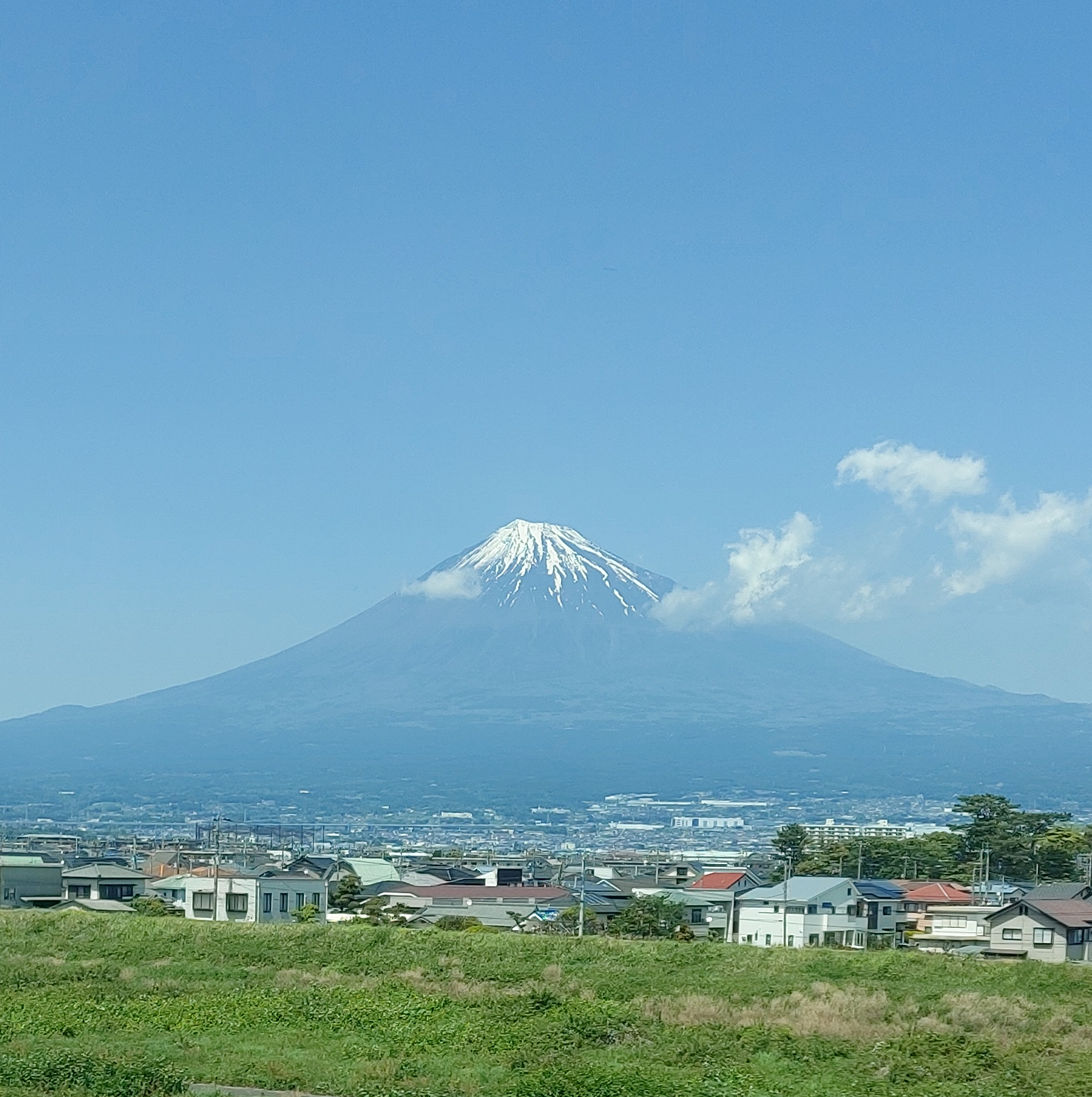
In Japanese, the word ‘Osaka’ also means ‘a large hill’. Japan’s geography has many large hills (see a picture of Mt. Fuji I took from the moving Shinkansen), and metaphorically speaking Japanese like to scale complex landscapes of life by bringing culture with science and technology. There is a lot to learn from this approach to life.

Osaka, optical manipulation and the perennial ascent towards knowledge. What a memorable trip this has been.
To Japan and to all the people I met here – Doumo Arigatou Gozaimasu !
Ocean, Okinawa and OIST…
I had a memorable visit to Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology – OIST (27th and 28th April 2023). Prof. Mahesh Bandi was my host, I had a fabulous time interacting with him and a few other groups. Below are some (of many) highlights.
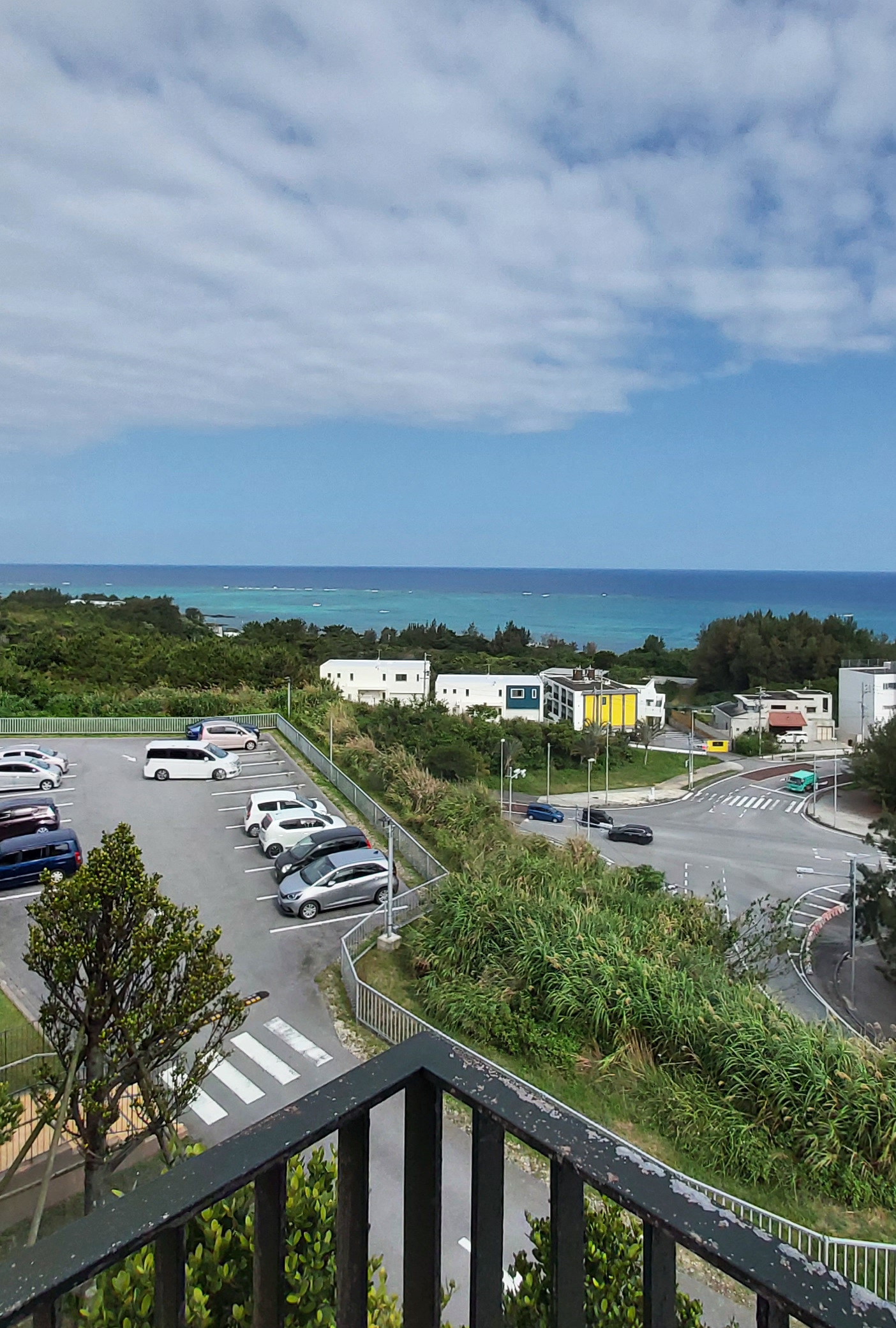
First, the geography : located in the midst of the ocean(s), away from the mainland Japan, Okinawa is the southern most part of Japan. I took a 2.5 hrs. flight from Tokyo and reached the destination when it was dark.

In the morning, I woke up and opened the window to be pleasantly surprised to see the beautiful ocean in my field of view. Below is a photo I took from the balcony of the room.

At the outset, I had a fabulous discussion. Mahesh and I had a excellent free-wheeling discussion on various topics including science, arts and history. Also, I visited his lab to see very creative experiments on non-equilibrium physics including some fascinating experimental designs to probe dynamics at liquid-air interface. He has a fabulous set of students working on interesting problems. It was both refreshing and stimulating.

In the afternoon, I gave my seminar and below is an interesting announcement (because it spells out my full name :-)). I discussed about some non-equilibrium aspects of our work, and towards the end emphasized some interesting prospects of statistical optics in an optothermal-assembly.

After my talk, I had illuminating discussion with Prof. Pinaki Chakraborty on thermal diffusion, fluid dynamics and history of science. I enjoyed visiting his lab, in which they have built one of the biggest Taylor-Couette flow set up I have ever seen (see the frame behind Pinaki in the picture below).
Next day, I had an elaborate lab tour of Prof. Sile Nic Chormaic, who is an expert in various topics related to optics/photonics including optical trapping. As she was travelling, her post-doc Dr. Souvik Sil, hosted me and took me around to show various aspects of their lab. It was a great learning experience.

On the same day, I visited the cutting-edge lab of Prof. Keshav Dani. Since he was travelling, his team members gave me a brief tour and I was amazed by some of their experiments.
Another major highlight of my trip was to meet many IISER students. Specifically, I met Amit Bhunia (post-doc) and Saurav Raj (PhD student) who are IISER Pune alumnus. I also met many IISER Kolkata students (Souvik being one of them).
Overall, I was mighty impressed by the research infrastructure at OIST and the people working there. It is quite remarkable how they have been able to build such a great facility in such a short time (their campus started around 2010).

Today, I have reached Osaka, and on Monday will be giving a talk and visiting a few groups at Osaka Unviersity. Prof. Hajime Ishihara is my host, and I look forward to plenty of interaction on optical manipulation.
Science + History —> better Science
I recently read an interview of Lorraine Daston, a reputed historian of science on “Does Science Need History?”
She was interviewed by the philosopher Samuel Loncar
The long-form discussion is about history of science and how and why it is relevant not only to the public but also to the practicing scientists.
In the later part of the interview , I found an interesting and important observation made by Lorraine :
“One of the greatest achievements of science, contrary to what anyone would have thought not just circa 1700 but circa 1800, is the creation of the only effective international governance system that we have. In the face of two planetary crises—climate change and a global pandemic—it has not been the UN, it has not been the G8, that got together to diagnose the problem and suggest a solution. It has been the international community of scientists, and I would be extremely loath in any way to undermine the only example of semi-effective international governance we have.”
This is probably one of the important comments on science I have come across in recent times. In an age where nation-states are still fighting (big and small) wars, this is indeed a profound reminder on what truly is the instrument of effective (inter)national governance.
Do check out the whole interview. It has many interesting strands, branches and discussion including philosophy of science, publishing and some great references to explore.
As I have mentioned previously in my blogs, part of the reason why I blog is to bring out the human side of doing science. Interviews like these reinforces this thought, and encourages me as scientist to look into the history of science as not something decoupled from the science itself, but as a part of ones research in understanding why we, as human beings, are interested in science. In my opinion, our science education (and research) will be vastly enriched by including and emphasizing history of science as integral part of science. Frequently, I have also found that some of the best commentaries and criticism on science as human endeavor emnating from historians of science.
After all, it was history of science which opened our eyes towards understanding the structure of scientific revolutions. Hence Science + History —> better Science, and perhaps better human beings !
Toys, Geim and Gupta
Recently I came across an editorial in Nature Physics, titled as Physics is our playground, which emphasized how playfulness has had an important role in some of the major inventions and discoveries in physics.
A particular example of this is the discovery of graphene, and how it has evolved into one of the most important topics in condensed matter science. Nowadays graphene is used as ‘Lego’ blocks to build higher order structures and the so-called ‘Van der Walls’ heterostructures are one of the most exciting applications of 2D materials. What started as a playful project in the lab has now turned out to be an important part of emerging technologies.
Two important inferences can be drawn from the playful attitude towards doing science :
First is that making modular elements and stacking them creatively can lead to emergence of new structures and function. Anyone who has used lego blocks can immediately relate to it.
Second is that toys are powerful research and teaching aids. Please note, that I emphasized research and teaching here. This is because toy-models are ubiquitous in research, and they help us create modular state of a problem in which unnecessary details are discarded and only the essential parts are retained. This way of thinking has been extremely powerful in science and technology (for example : see ball and stick models in chemistry and mega-construction models in civil engineering )
When it comes to toys and education, there is no better example than the remarkable Arvind Gupta (see his TED talk). His philosophy of using toys as thinking aids is very inspiring. Being in Pune, I have had a few opportunities to attend his talks and interact with him (as part of an event at science activity center at IISER-Pune), and I found his approach both refreshing and implementable. Importantly, it also showed me how creativity can emerge from constraints. To re-emphasize this, let me quote APS news article on Andre Geim :
“Geim has said that his predominant research strategy is to use whatever research facilities are available to him and try to do something new with the equipment at hand. He calls this his “Lego doctrine”: “You have all these different pieces and you have to build something based strictly on the pieces you’ve got.””
Now this is an effective research strategy for experiments in India !
Chomsky et al., on Chatgpt
Chomsky et al., have some very interesting linguistic and philosophical points on chatGPT/AI and their variants (see NYT link).
To quote
“The human mind is not, like ChatGPT and its ilk, a lumbering statistical engine for pattern matching, gorging on hundreds of terabytes of data and extrapolating the most likely conversational response or most probable answer to a scientific question. On the contrary, the human mind is a surprisingly efficient and even elegant system that operates with small amounts of information; it seeks not to infer brute correlations among data points but to create explanations.”
The philosophical and ethical viewpoints expressed in this article are indeed noteworthy. What probably is even more important is the linguistic viewpoint which amalgamates language with human thought process, and that is what makes this article more interesting and unique.
My own take on Chatgpt has been ambivalent because I do see tremendous potential, but also some obvious faults in it. About a couple of months ago, I did try to play around with it, especially in the context of some obvious questions I had on optical forces, and the answers I got were far from satisfactory. At that time, I assumed that the algorithm had some work to do, and it was probably in the process of learning and getting better. The situation has not changed for better, and I do see some major flaws even now. Chomsky’s article highlighted the linguistic aspects which I had not come across in any other arguments against artificial intelligence-based answer generators, and there is some more food for thought here.
This is indeed an exciting time for machine learning-based approaches to train artificial thought process, but the question remains whether that process of thought can somehow emulate the capabilities of a human mind.
As humans, a part of us want to see this achievement, and a part of us do not want this to happen. Can an artificial intelligence system have such a dilemma?
Basic advice to undergrads: written assignments
Below is some basic advice I shared with my undergraduate class (Physics majors/Optics). This may be useful to other students here.
- Do not copy a text verbatim, unless you are quoting the text as it is, with reference at that location. If you use a source, then write a summary in your own words and cite the original source at the location of your text.
- In the absence of primary data (which you generate originally), you will be using secondary sources such as research papers, books and internet content. For scholarly purposes (including assignments), it is better to use journal articles and books as references. Wikipedia is essentially a tertiary reference. Although some entries are good, wikipedia content is generally taken from a book or a research paper. Identify that source and use it for your assignment and reference. Directly citing wikipedia (which is usually not peer reviewed by experts) is not a general practice in scientific literature.
- When you take a figure or equation from a secondary resource (paper, book, internet), it is important that you cite the source in figure caption/equation location.
- In an assignment, I am mainly interested in reading what you think about the topic under consideration. Feel free to put down your thoughts and compare and contrast it to the literature you use. This is where the thinking + learning happens.
- For some general advice on referencing, especially for online communication, have a look at my blogpost.
- To appreciate importance of written communication in learning, have a look at another blogpost.
12 Years as a faculty member in India – 12 lessons
Today I complete 12 years as a faculty member at IISER-Pune. I have attempted to put together a list of some lessons that I have learnt so far. A disclaimer to note is that this list is by no means a comprehensive one, but a text of self-reflection from my viewpoint on Indian academia. Of course, I write this in my personal capacity. So here is it..
- People first, infrastructure next – As an experimental physicist, people and infrastructure at working place are of paramount importance. When I am forced to prioritize between them, I have chosen people over infrastructure. I am extremely fortunate to have worked with and continue to work with excellent students, faculty colleagues, and admin staff members. I think a good work place is mainly defined by the people who occupy it. I am no way neglecting the role of infrastructure in academia, especially in a country like India, but people have a greater impact in academic life than infrastructure.
- Create internal standards – In academia, whether you like it or not, there will be evaluations and judgments on your research and teaching. Generally, every academic ecosystem has its own standards for evaluating people. These standards are generalized principles and are not customized to an individual. Therefore, it was important for me to realize what good work meant and how to judge myself. As long as internal standards are high, and are properly met with consistency, the external evaluation becomes secondary. This attitude totally frees up the mind, and helps me to get better compared to my previous self. This also means I can appreciate others work without having to compare myself to them.
- Constancy and Moderation – When it comes to any work, it is important to be consistent over a long period of time. An equally important aspect is to moderate the amount of work done for a period. Most of the important work in research happens in units of months if not years. Therefore, constant effort with moderation keeps the motivation high, and makes the work enjoyable. Binge-working is attractive, but for intellectual work it is ineffective.
- Writing is a great tool to think – One of the most underestimated tools of thinking is writing. Not just formal writing, but the process of external articulation of thought on paper does wonders. Countless times, I have obtained, clarified and developed my thoughts only after I started writing about it. Writing is integral part of research and not just a communication tool.
- Importance of philosophy – Ever since I was an undergrad, I have been interested in philosophy of science. I had never taken a formal course on philosophy, but I have gradually started appreciating the role of philosophy of science. Specifically, it has catered to my question on ‘why I do what I do?’
- Teaching as social responsibility – In the Indian academia, scientific social responsibility is a buzz word. For me, the greatest social responsibility as an academic comes in the form of teaching. In larger scheme of things, some how we tend to neglect the impact of conventional teaching on students. Also, this impact is not easily measured. But the joy one obtains seeing a student do well is priceless. This local impact is what I value more because the feedback is there to see, right in front of you.
- Science, sports and arts : a trinity – I love outdoor sports including running, swimming, cricket etc. Equally, I enjoy listening to music, reading poetry and appreciating any form of art from any culture. I have found that it has not only made me a better person, but also has positively impacted my work. Taken as a trinity, these human endeavours continue to enrich our lives.
- Emphasis on mental and physical health – The most important policy that I have set in my research group is this: To do effective and enjoyable work, your mental and physical health should be good. There is no point in doing good work at the expense of your health. Therefore the priority will always be good health followed by good work.
- Social media : effective if used properly – Social media has a unique reach. If you are in India, and you want to connect to the scientific world, social media is an excellent platform. Given the size and diversity of India, social media can also reach people from various backgrounds and languages. If used responsibly, social media can have great impact on how science is communicated within India and how India connects to the scientific world.
- Renewed interest in applied mathematics and coding – During my BSc (Maths, Physics, Electronics) and MSc (Physics), I had excellent training and exposure in mathematics. During the lock-down period, I rejuvenated my interest in applied mathematics (especially nonlinear dynamics) and have started coding too. This has added a new impetus to my research and should reflect in the coming years.
- Professor as a post-doc – A research strategy I found useful in my work is to treat myself as a post-doc in the lab. Given that, in India retaining a long-term post-doc is difficult, many of the skills and thought processes cannot be effectively transferred in lab. A long term research problem needs sustained effort in the lab. As an experimental faculty it is easy to get caught up in activities outside the lab and lose touch with the (optical) bench work. Thanks to the lock-down period, I was the only one in the lab for almost 6 months,and I restarted my experimental work. I value that time and I see great benefit in this approach.
- Self-mentoring – A lot of academic advice is written by people working in the west. A few of them are general and applicable to Indian academia, but many of them are not. In such a situation, as an academic I try to derive inspiration by reading, especially about people who have done great work in India. I have been deeply influenced by people such as M. Visvesvaraya and Ashoke Sen.
Scientific Philosophy and Mental Health
Many a times, we are oblivious to the impact that Science has on an individual mind. It gets drowned in the collective impact. Curiosity is probably the most natural feeling of humans. If done right, Science cultivates and elevates this feeling. It may positively impact mental well-being too.
Increasingly, in Indian academia, mental well-being of all the stakeholders (students, faculty, admin etc.,) has emerged as an urgent and important issue that needs attention. Especially in a country such as India, where a loose order emerges out of chaos in almost all aspects of life, it is important to stay connected with oneself. Scientific curiosity may cater to this vital need.
The connection with oneself via science, or broadly speaking with any form of curiosity (arts/sports), is something we must harness. A major part of human development is to connect with oneself AND with the society. In this age of social media, sometimes, we may forget the former and focus only on the later. We will have to remind ourselves that being curious about anything is not being ‘childish’ but being human. Scientific curiosity and questioning is fundamental to our living, and this affects everything we do in our life.
To conclude let me quote from Bertrand Russell’s The Value of Philosophy :
“Philosophy is to be studied, not for the sake of any definite answers to its questions, since no definite answers can, as a rule, be known to be true, but rather for the sake of the questions themselves; because these questions enlarge our conception of what is possible, enrich our intellectual imagination, and diminish the dogmatic assurance which closes the mind against speculation; but above all because, through the greatness of the universe which philosophy contemplates, the mind also is rendered great, and becomes capable of that union with the universe which constitutes its highest good.”
Science as in philosophy, does cater to the highest good of humanity. What we under-appreciate is that it goes beyond the call, and impacts an individual’s mind. Academia should be a place to foster such an impact at various levels: individual, local and global. Perhaps that is the meaning of an “University”.