During the formative years of quantum mechanics (early 1900s), the spin and orbital angular momentum of atoms were found to be quantized by theoretical arguments. Experimental proof was lacking.
Stern-Gerlach experiment provided the first experimental proof in 1922. They took a beam of neutral silver atoms and deflected them through an inhomogeneous magnetic field.
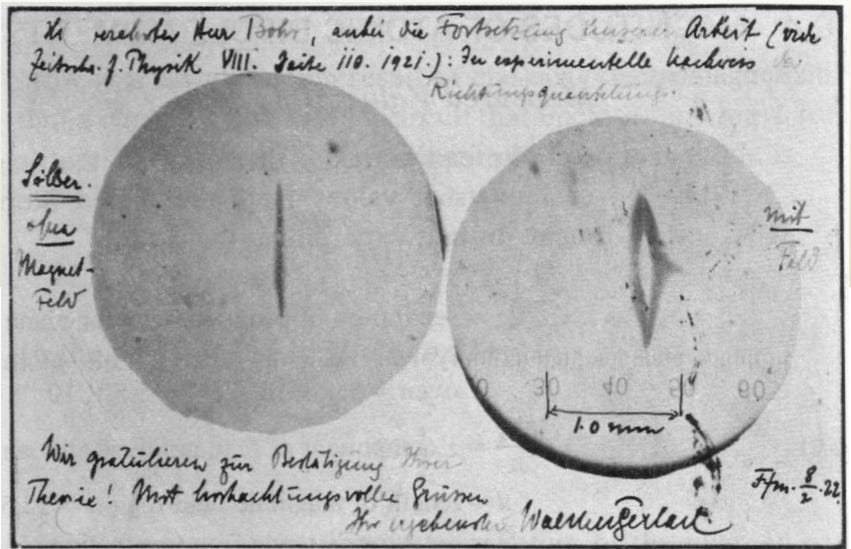
Silver atoms have an unpaired electron in their outermost orbit. If they were to obey quantum mechanics, they should exhibit a spin of +1/2 or -1/2. When subjected to an external magnetic field, the electrons with +1/2 or -1/2 should spatially split into two. That is exactly what Stern and Gerlach observed, and below is the first picture of the same.
To quote the authors:
Gerlach’s postcard, dated 8 February 1922, to Niels Bohr. It shows a photograph of the beam splitting, with the message, in translation: “Attached [is] the experimental proof of directional quantization. We congratulate [you] on the confirmation of your theory.” (Courtesy AIP Emilio Segrè Visual Archives.)
This experiment was one of the most important observations in quantum mechanics and further confirmed the quantization of spins, which is now common knowledge in physics.

