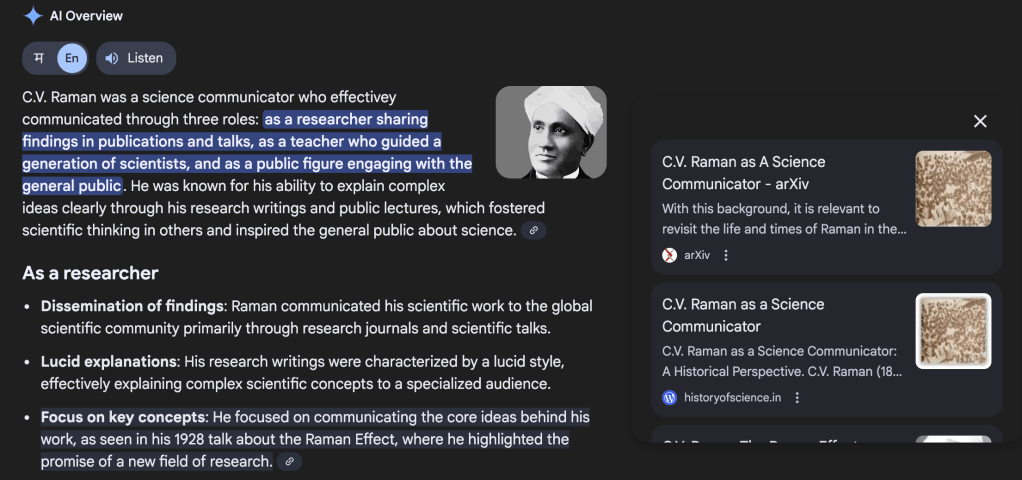
I see that the essay I wrote on CV Raman and made open access (thanks to Resonance, which published it) has been used by several educators on YouTube, including some in Indian languages. Also, the Google AI overview shows the published essay as the main reference for a search related to Raman’s science communication (see slideshow below).
I am glad to see that making one’s writing open to all has positive effects. Open-access, not just for readers, but also for authors, is beneficial. Especially in India, paywalls for science are a detriment.
My worry is that open-access publishing has been mainly driven by commercial publishers that extract huge funds from the publishing authors. This defeats the purpose of open science, especially when the research of an author is publicly funded. Added to that, Indian researchers and writers cannot afford to pay huge sums for publishing articles and books.
The publication landscape (including journals and books) across the world needs an introspection. Open-access model is effective only when the readers and authors have access to that model. Otherwise, the model becomes a paywall for authors.